Historic Sites
Marked by the National Heritage Board
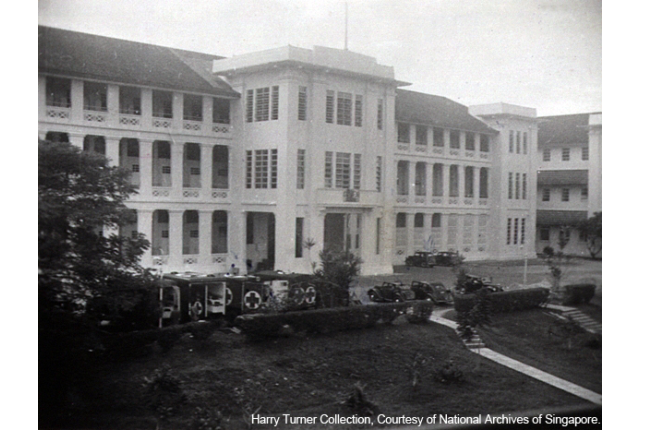

Alexandra Hospital
Alexandra Hospital, opened in 1940, stands on the site of an earlier Alexandra Indian barracks which was established around 1908. The new military hospital was built to serve the increased number of British troops stationed in Singapore, as part of British preparation for a war in Singapore.
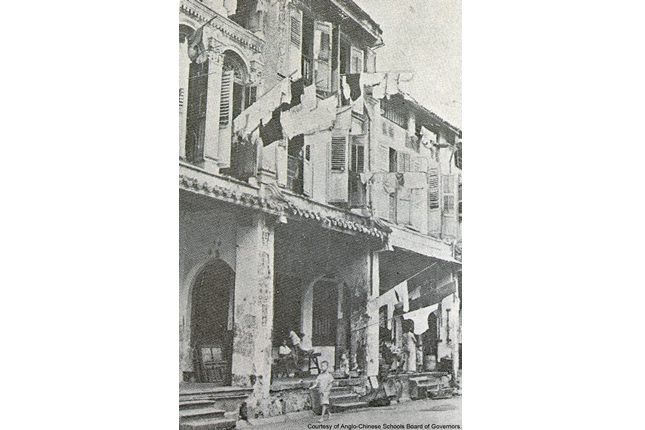

Anglo-Chinese School
The Anglo-Chinese School (ACS) was founded by Rev. William Fitzjames Oldham in 1886 at a shophouse in Amoy Street. Starting with 13 students, the school aimed to provide an education for the many boys Bishop Fitzjames saw wandering aimlessly in the streets.

Balestier Plain
Balestier Road, from which Balestier Plain takes its name, was named after Joseph Balestier, a keen botanist and agriculturist who arrived in Singapore in 1834.

Battle at Adam Park
Adam park estate was the site of intense fighting between British forces and the invading Japanese army in February 1942, in the last days before the British surrendered Singapore.

Battle at Kranji Beach
Kranji Beach Battle was one of the battles in the defence of Northwestern Singapore between the Australian 22nd Brigade and the Japanese Imperial Guards Division.

Battle at Pasir Panjang
The Battle at Pasir Panjang, where the harbour and British military depots were the coveted gains, marked one of the last battles for Singapore. It lasted from 12 to 14 February 1942.
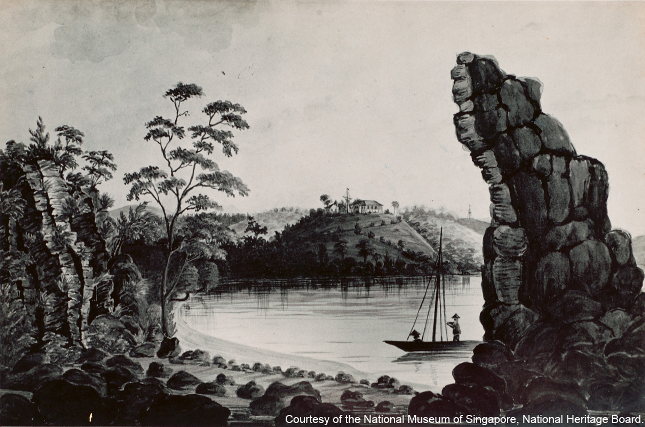

Batu Berlayar
A craggy granite rock outcrop known in Malay as "Batu Berlayar" ("Sailing Rock") used to stand on this shore. Another rock outcrop also used to stand on the opposite shore of Tanjong Rimau on Sentosa Island.
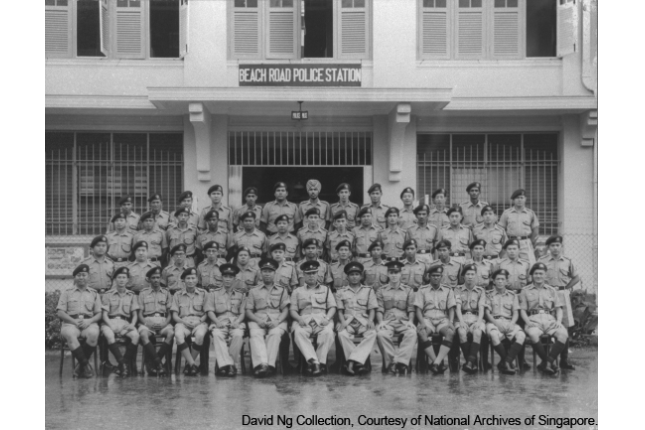

Beach Road Police Station
In the early 1900s, Singapore grew rapidly and the crime rate rose with the city's expansion. Harold Fariburn - the Inspector - General of Police from 1925 to 1935 - realised that the Police needed a programme of modernisation and expansion.
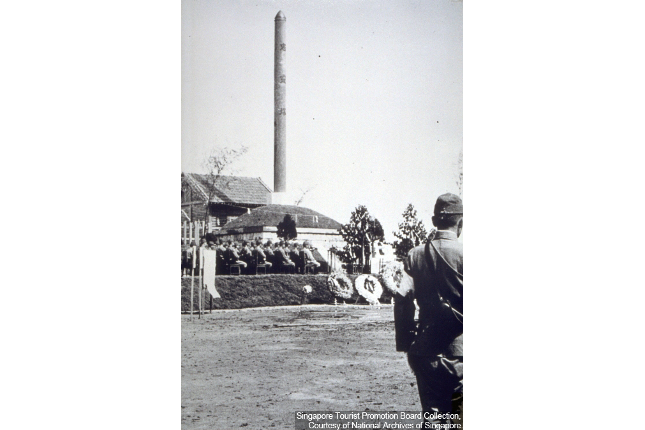

Bukit Batok Memorials
Two memorials, one for the Japanese soldiers and the other for Allied Soldiers sat on top on this hill-top. The former was Syonan Chureito, built by 500 Allied Prisoners of War while the latter was a wooden cross that stood behind.

Battle at Bukit Timah
One of the fiercest military encounters during WWII took place here as the Bukit Timah area held strategic and tactical importance to the Japanese and the British.
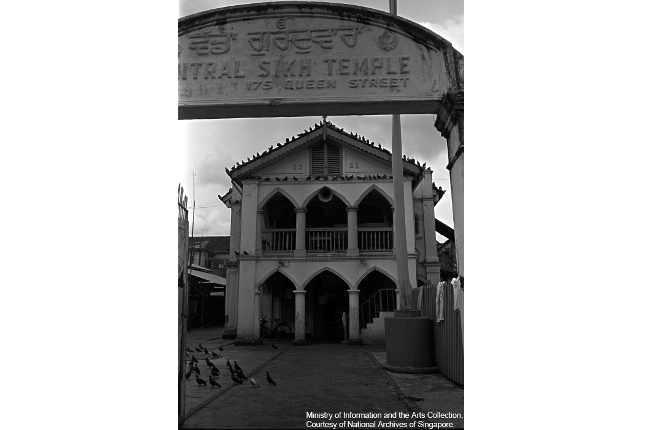

Central Sikh Temple
Also known as the Wadda Gurdwara, this Sikh temple was the first set up in a bungalow at Queen Street in 1912. The temple is now relocated at Towner Road.
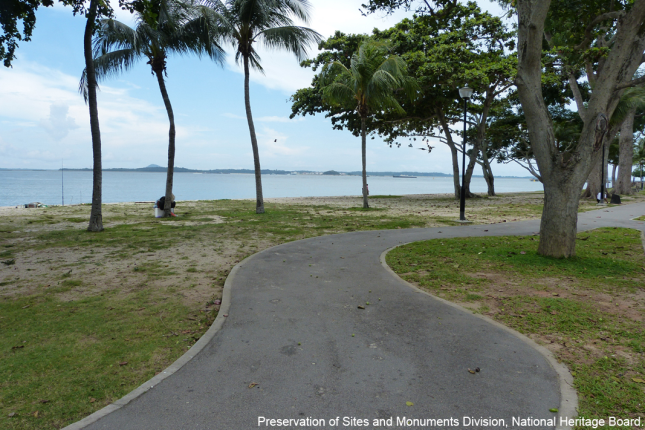

Changi Beach Massacre
66 Chinese male civilians were killed by Japanese hojo kempei (auxiliary military police) firing squads at the water's edge on this stretch of Changi Beach on 20 February, 1942.

Changi Murals
The Changi Murals, located at Block 151 of Changi Camp (Martlesham Road), were symbols of the hope and faith of Prisoners-of-War (POW) interred in the camp during the Japanese Occupation (1942-1945).

Chen Wen Hsi Historic Marker
One of Singapore’s first-generation artists, Chen Wen His's body of work is internationally and locally acclaimed.
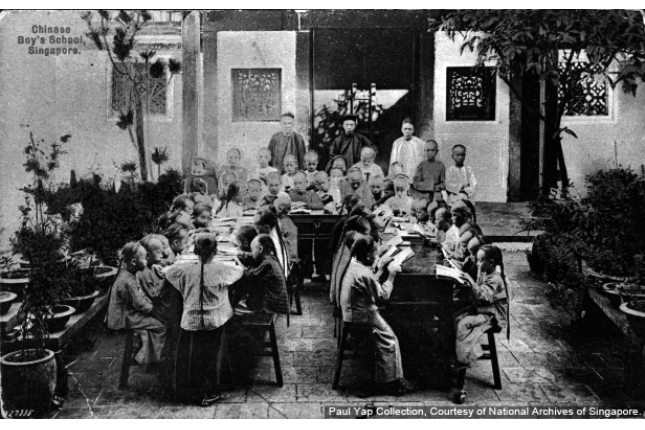

Chui Eng Free School
Also known as the Chinese Free School, this school for boys in the Hokkien community was built in 1854 and endowed by Tan Kim Seng, a wealthy Straits Chinese merchant. It closed down in 1954.
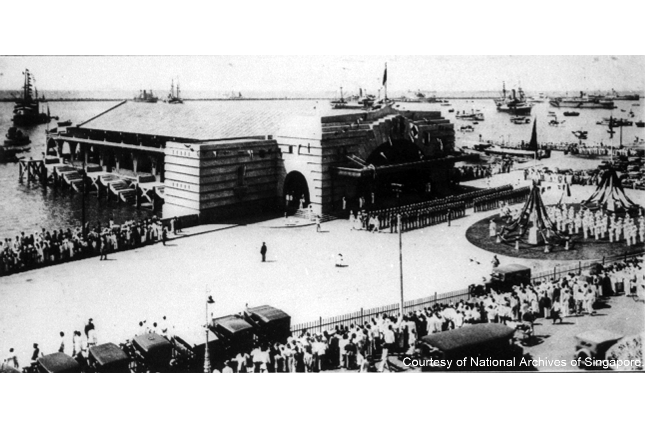

Clifford Pier
Clifford Pier was the landing point of sea passengers and immigrants who came to seek a new life of hope in Singapore.
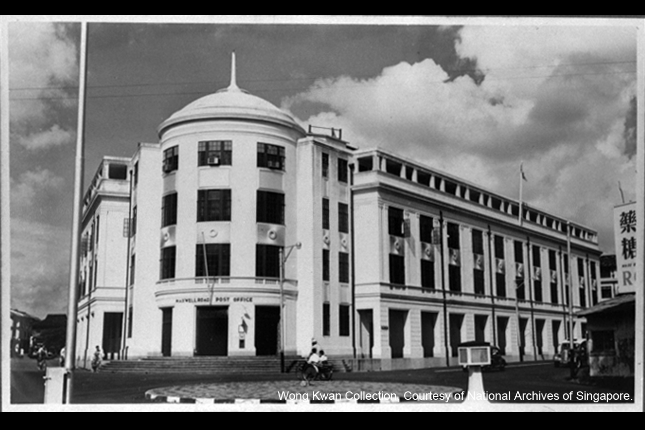

Custom House, Maxwell Road
Custom House is representative of the style and architecture of buildings designed by the PWD under the leadership of Frank Domington Ward, the Chief Architect.
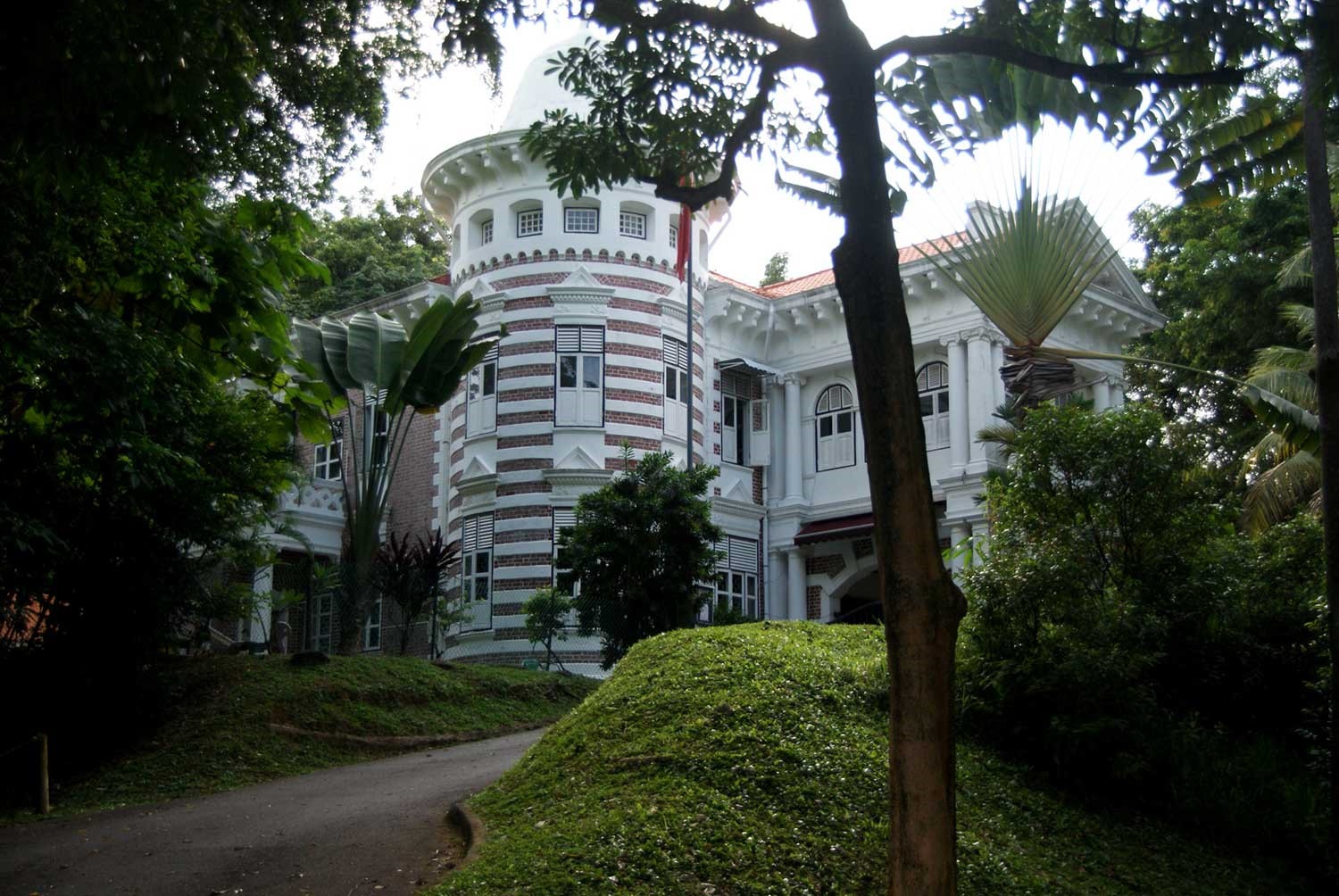

Danish Seamen's Church (Former Golden Bell Mansion)
Completed in 1910 by philanthropist Tan Boo Liat, great-grandson of Tan Tock Seng, the former Golden Bell Mansion was named after Tan Boo Liat’s grandfather Tan Kim Ching, whose name means golden bell.
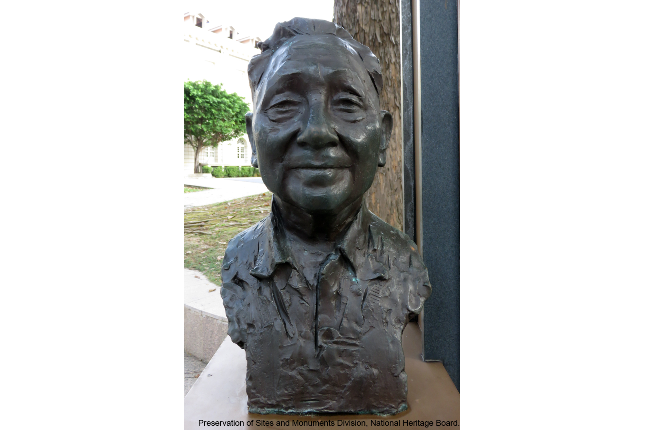

Deng Xiaoping Historic Marker
Originally known as Deng Xiansheng and his school name Deng Xixian, Deng Xiaoping was born on 22 August 1904 in Guang'an County, Sichuan Province.
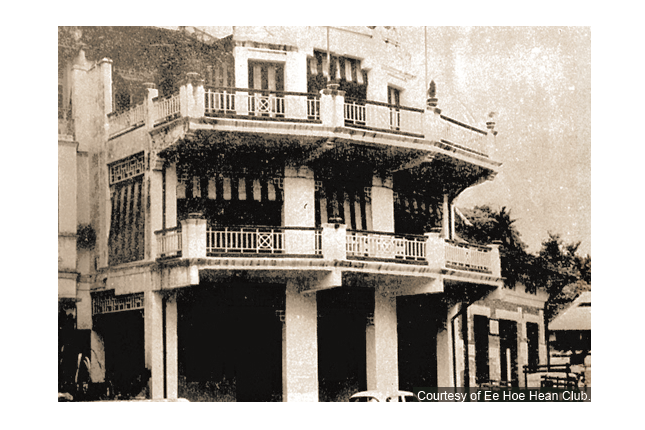

Ee Hoe Hean Club
Founded in 1895, it is one of the oldest millionaires club in Singapore. The club was the centre of the Chinese Salvation Movement in Southeast Asia from 1937-1942. Originally located at Duxton Hill, it moved to Club Street before settling at this location in 1952.
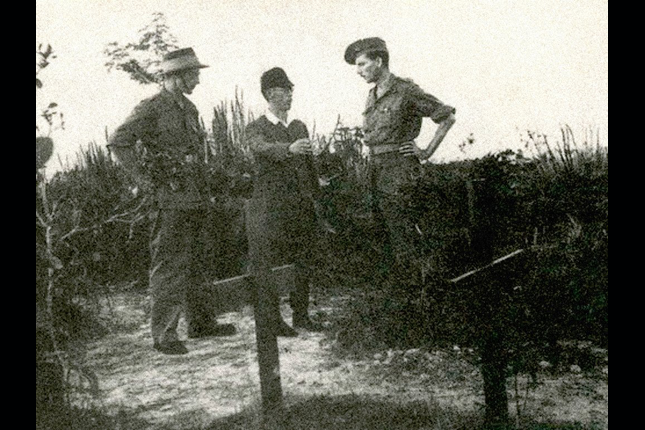

Execution of Captured Rimau Commandos Historic Marker
Operation Rimau (“tiger” in Malay) was the second Allied commando attack that targeted Japanese ships in Keppel Harbour. It took place from late September to early October 1944 during the Second World War.
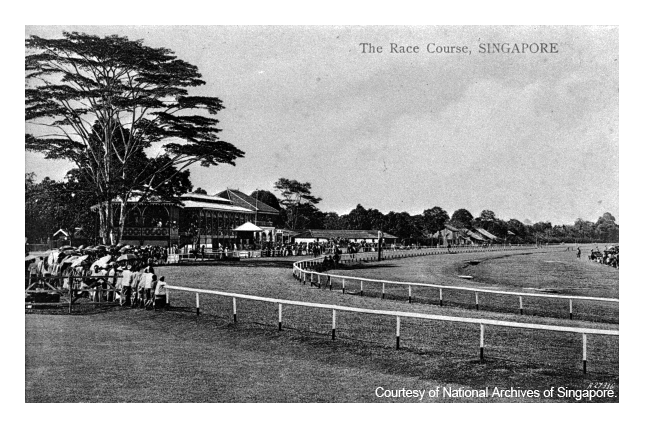

Farrer Park Field
This was the site of the first race course in Singapore. It held weekly horse races and was a popular recreational place among European residents.
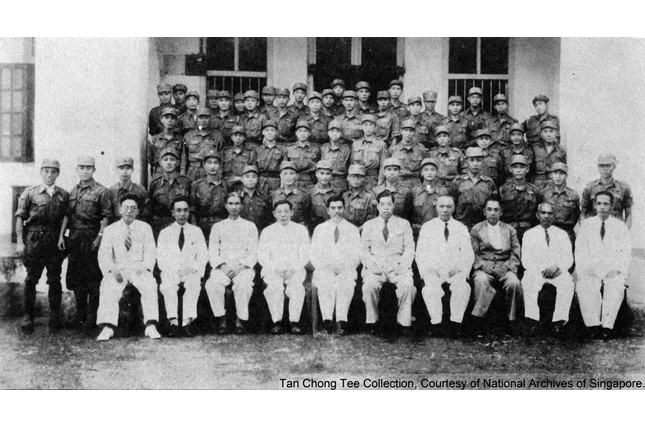

Force 136 Historic Marker
Force 136 was a British secret service team that operated in Malaya during the Second World War. One of the agents was Lim Bo Seng, who led Gustavus V Operation in 1943. His grave is in the vicinity.
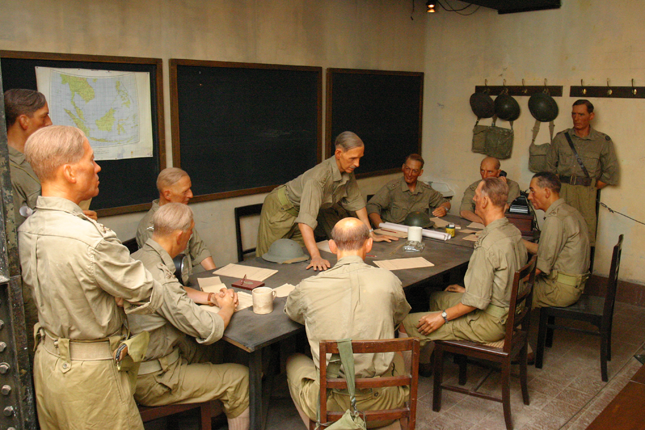

Fort Canning Command Centre
Fort Canning Command Centre comprises an underground fortress network of bunkers and tunnels. It was constructed in the late 1930s to serve as a combined command and control centre for the British and Allied forces in Malaya.
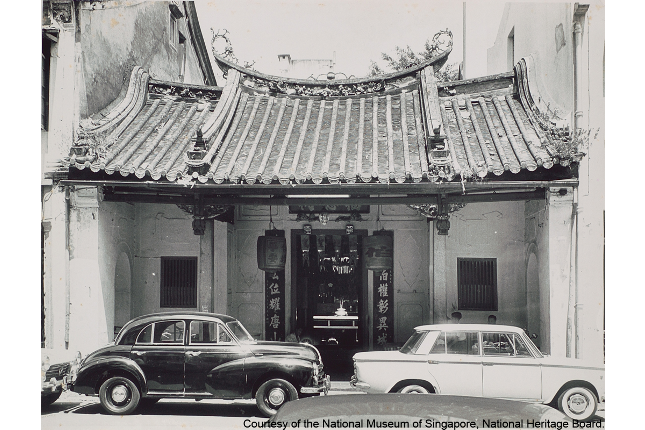

Fuk Tak Chi
Reputedly the first Chinese temple in Singapore, it grew from a small shrine set up here by the Hakka and Cantonese immigrants in 1824. The temple also became an association that looked after the interest of the two dialect groups.
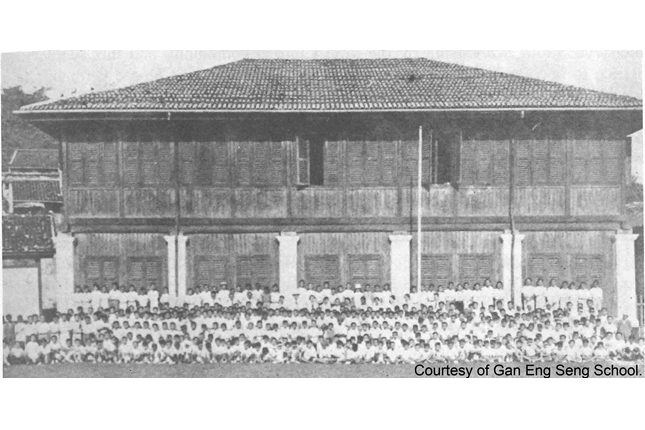

Gan Eng Seng School
In 1885, Gan Eng Seng founded a free school for poor boys in Singapore. Initially named the Anglo-Chinese Free School, it was among the earliest schools to offer a bilingual education. The school moved to its first new building about 50 metres behind Telok Ayer Chinese Methodist Church in 1893. It became known as Gan Eng Seng School in 1923.
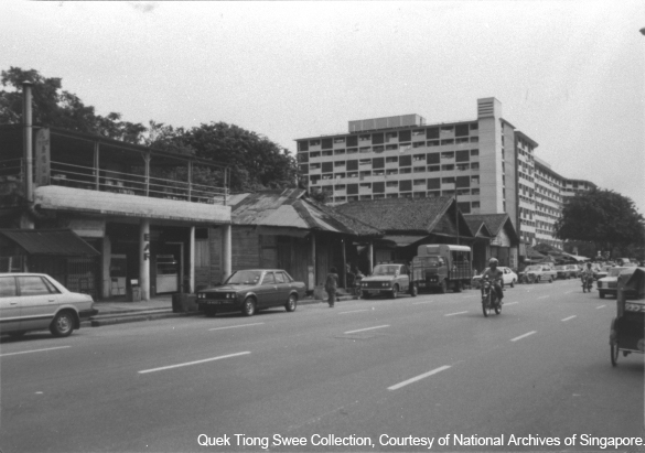

Geylang Serai
Geylang Serai is the social centre of the Malays in Singapore. This once agricultural area was known for the fragrant lemon grass - Serai - grown as a cash crop by the Malays who were resettled from the Singapore River mouth in the 1840s. The name Geylang Serai is said to be derived from a lemon grass factory "Kilang Serai" located east of Kallang River.
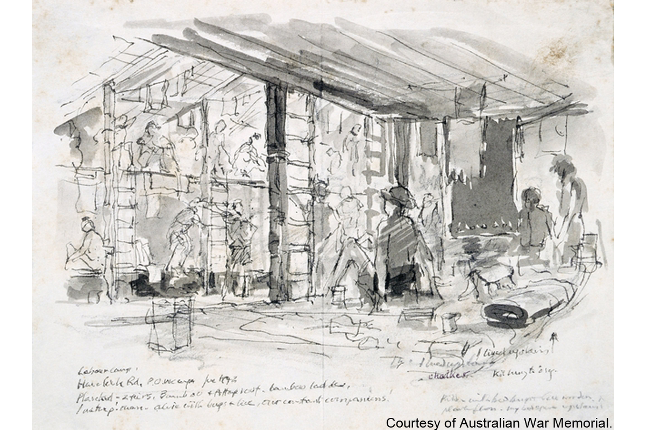

Havelock Road Camp / River Valley Road Camp
The area bounded by River Valley Road and Havelock Road was occupied by Prisoner-of-War (POW) camps during the Japanese Occupation (1942-1945). The Havelock Road/River Valley Road camps comprised groups of dilapidated attap huts which housed thousands of POWs.

Indian National Army Memorial
This World War Two plaque was erected in 1995 to mark the site of the original Memorial, dedicated to the "unknown warrior" of the INA and to the other INA members who were involved and killed in the fighting in Burma.
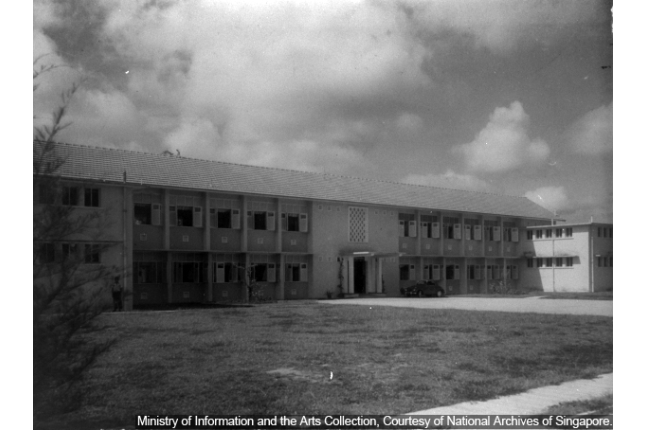

Institute of Mental Health
Established in 1928 as The Mental Hospital, off Yio Chu Kang Road. Convalescent Hospital during WW2. Named Woodbridge in 1951 after a wooden bridge. Expansion during 1950s-70s. Moved to new premises at Buangkok View in 1993.
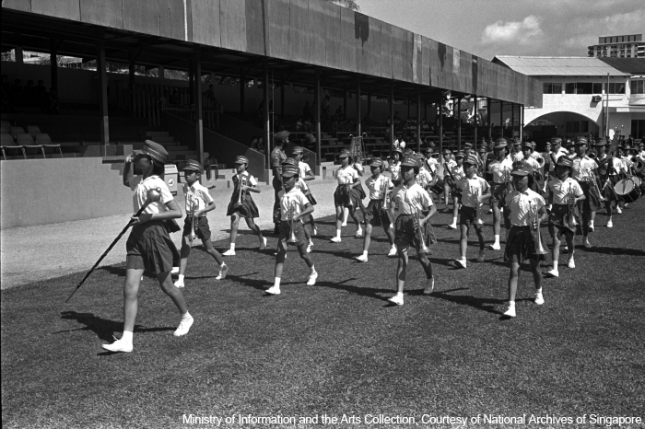

Jalan Besar Stadium
Jalan Besar Stadium was Singapore’s main football arena until the National Stadium opened. It also hosted various national events, such as Singapore Youth Festival and National Day Parade.
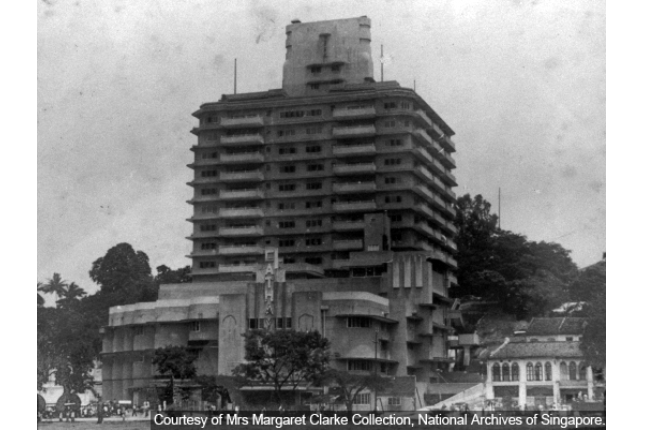

Japanese Propaganda Department Headquarters
Formerly housing the British Malaya Broadcasting Corporations before WWII, it was turned into a Japanese propaganda office during the Japanese Occupation. It was later also used by Lord Louis Mountbatten as the headquarters for the Japanese Surrender in 1945.
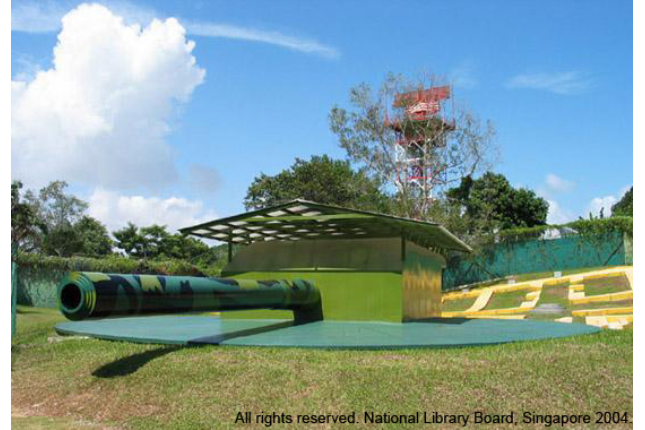

Johore Battery
Johore Battery was built in the late 1930s as part of Singapore’s coastal defence system. It comprised three 15-inch guns, known as “monster guns”. Although the battery was meant to stop enemy attacks from the sea, two of its guns could be rotated to fire landward.
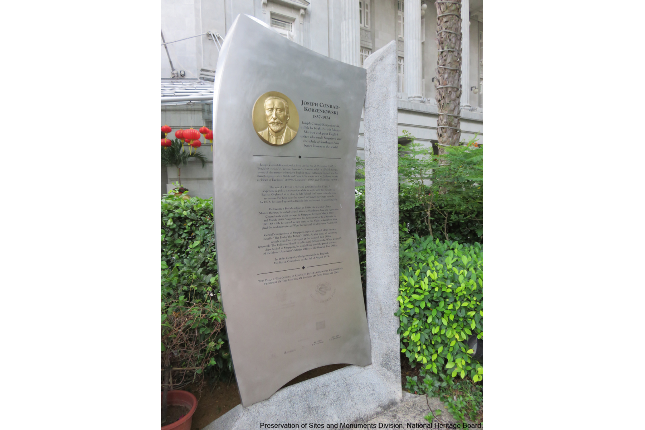

Joseph Conrad Historic Marker
Joseph Conrad, the renowned English master writer, was of Polish origin and travelled to Singapore and south east asia during his seafaring days. He made Singapore and Southeast asia better known to the world through his writings.

Jurong-Kranji Defence Line
This was an arbitrary defence line from Kranji River to Jurong River, placed to check Japanese advance towards the city from the west.
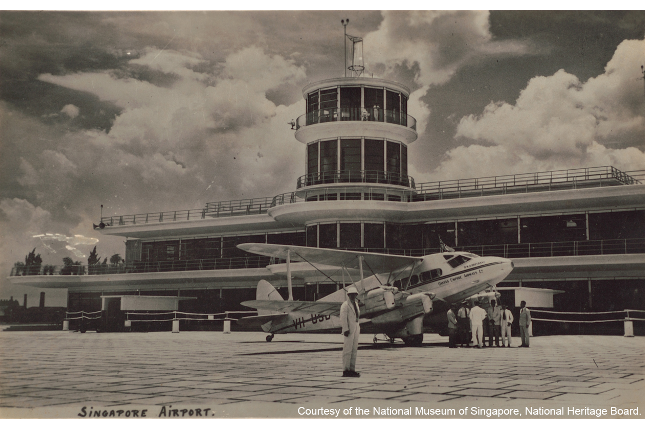

Old Kallang Airport
On 1 July 1960, the People's Association took over its main building as its headquarters and remained there till April 2009.
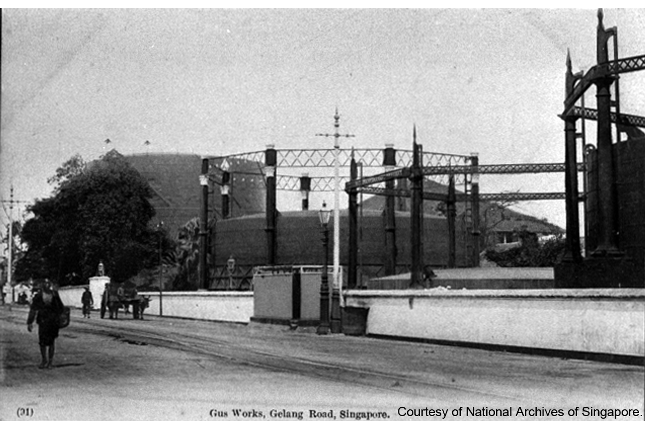
Kallang Gasworks
Back in 1861 when piped gas was first introduced, gas was produced using coal as a feedstock. Kallang Gasworks' location by the bank of Rochor River was an ideal choice for easy delivery of coal by boat from neighbouring countries.
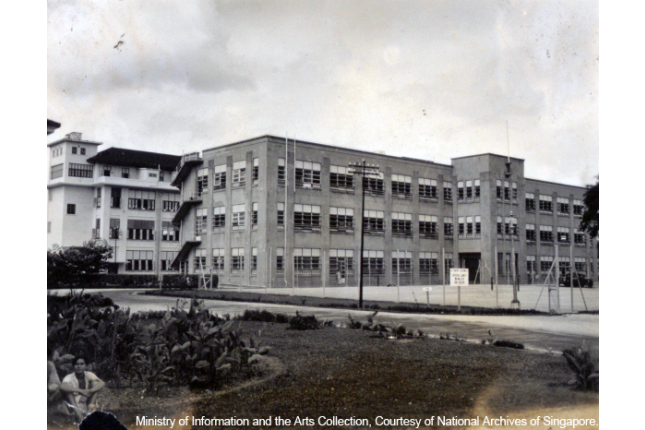

Former Kandang Kerbau Hospital
Kandang Kerbau Hospital, the birthplace of over 1.2 million Singaporeans, was the largest maternity hospital in the world from the early 1950s to the early 1970s.
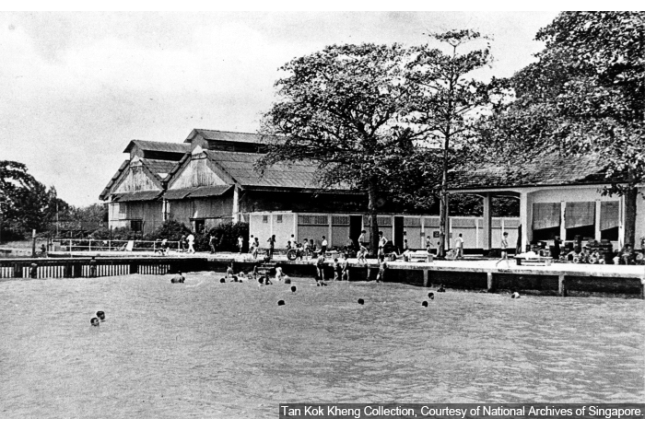

Katong Park
Built in the 1930s, Katong Park was the site of a bomb explosion on 24 September 1963. This marked the beginning of Konfrontasi (confrontation) when Indonesia, led by Sukarno, opposed the formation of Malaysia which, until 1965, included Singapore.
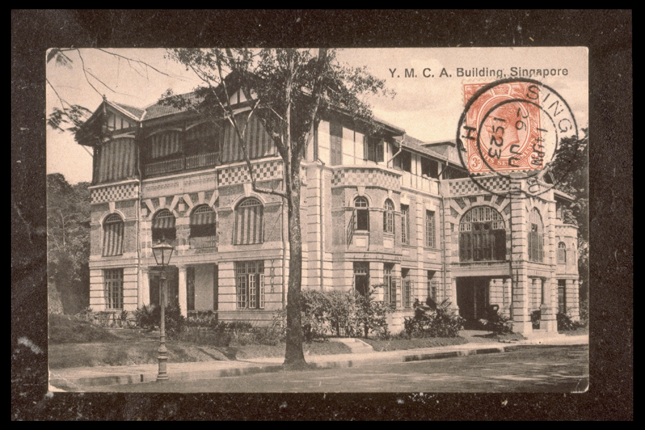

Kempeitai East District Branch
The original building, the YMCA, was used by the East Branch of the Kempeitai (Japanese Military Police) during the Japanese Occupation.
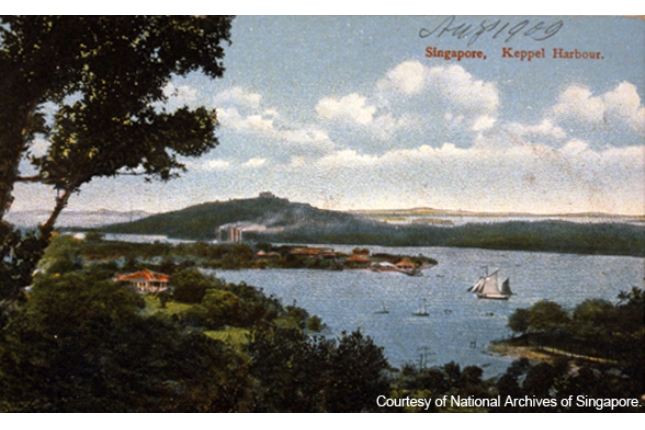

Keppel Harbour
Keppel Harbour has been a thriving maritime gateway for international trade since the late 19th century. It was originally known as New Harbour and was renamed in honour of Admiral Henry Keppel in 1900. From 1939 to the early 1940s, Allied soldiers came through this harbour to strengthen the defence of Singapore and the rest of Malaya.
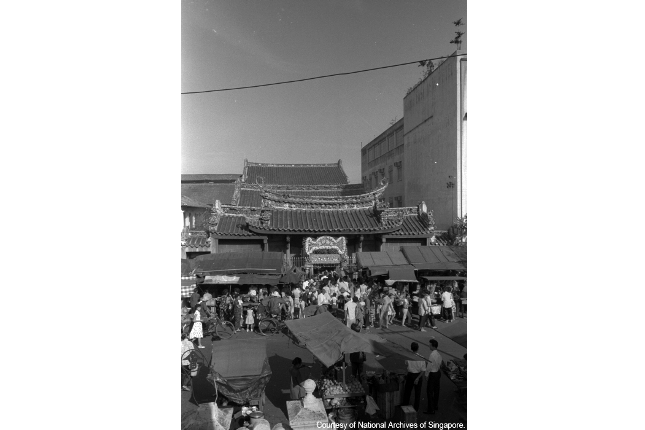

Kwan Im Thong Hood Cho Temple
This temple was built in 1884, showcasing a fine example of Chinese temple architecture and traditional craftsmanship. The temple played an important role in providing refuge for the sick, the wounded and the homeless during the Japanese Occupation.

Labrador Battery
This is one of the surviving gun emplacements in Singapore today. The battery has two 6” 16-ton guns facing south, which aided the Malay Regiment in the Battle for Pasir Panjang by firing high explosive shells at the advancing Japanese troops along the coast.
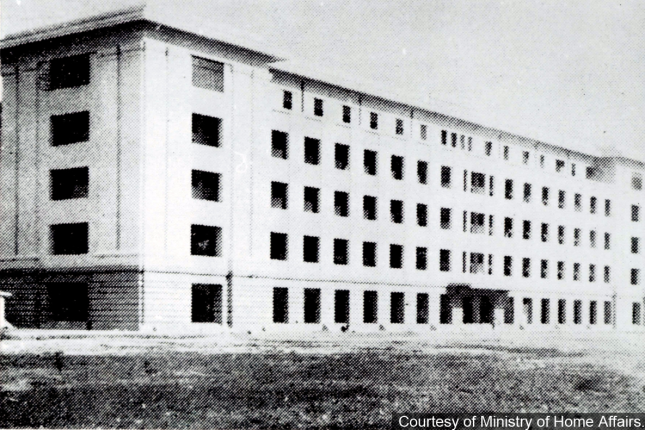

Former Lower Barracks
From 1881, Sikh men began arriving in Singapore as part of the Straits Settlement Police’s Sikh Contingent. Along with the Upper Barracks at the top of this hill, this 5-Storey building was completed in 1934 to house the men.
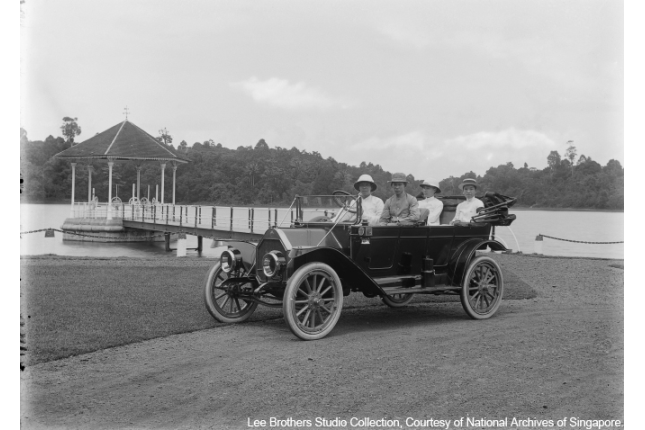

MacRitchie Reservoir
Completed in the 1860s, this reservoir was part of the first public water supply system implemented in Singapore. Its construction was assisted by the financial contribution of Tan Kim Seng, a straits Chinese merchant.
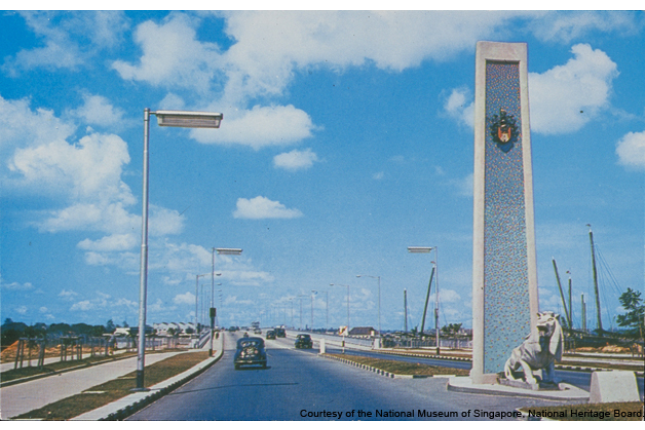

Merdeka Bridge
This bridge, the first to be built after the Japanese Occupation, was a sign of Singapore’s growing affluence and hope for a properous future. Officially opened on 17 August 1956, the 2,000-foot structure was the longest pre-stressed bridge in Southeast Asia.
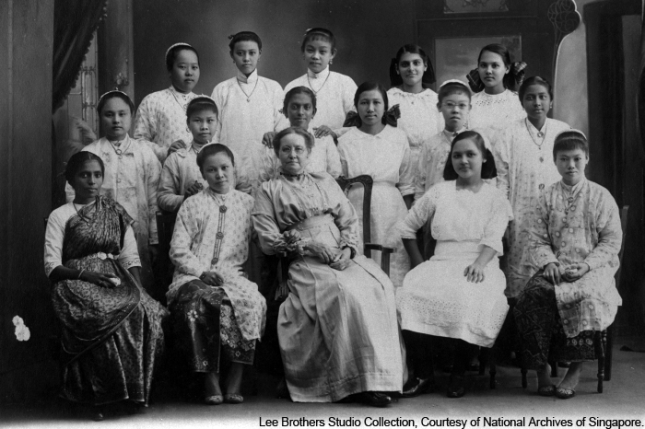

Methodist Girls' School
Founded in 1887 by Miss Sophia Blackmore, an Australian missionary, the school began as Tamil Girls’ School in Short Street with an enrolment of 9 Indian girls.
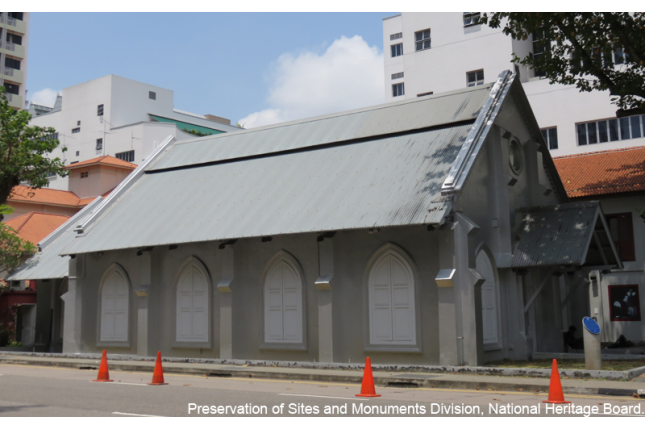

Middle Road Church
Built between 1870-75, the Middle Road Church was first known as the Christian Institute. When it was officially inaugurated as the Malay Church in 1894, it became the first Straits Chinese Methodist Church in Singapore.
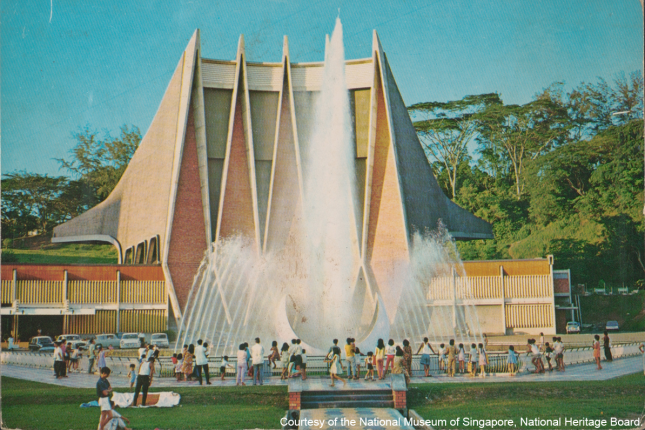

National Theatre
Officially opened on 8 August 1963, this theatre was built to commemorate the attainment of Singapore’s self-government in 1959. It was demolished in 1986 due to structural reasons.
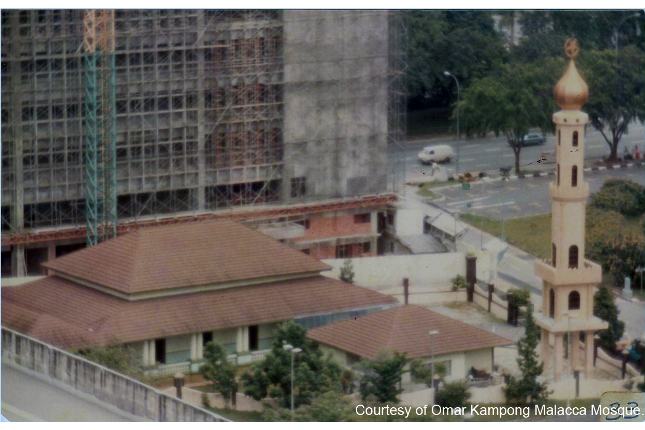

Omar Kampong Malacca Mosque
Established in 1820, Omar Kampong Malacca Mosque is Singapore’s oldest mosque. In the 1850s, the original timber structure made way for the current building to accommodate the mosque’s growing needs.

Outram Road Prison
Built in 1847, this is Singapore’s first civil and only large prison facility until Changi prison was build in 1936. It was also the first regular female prison and was once used for the public execution of prisoners.
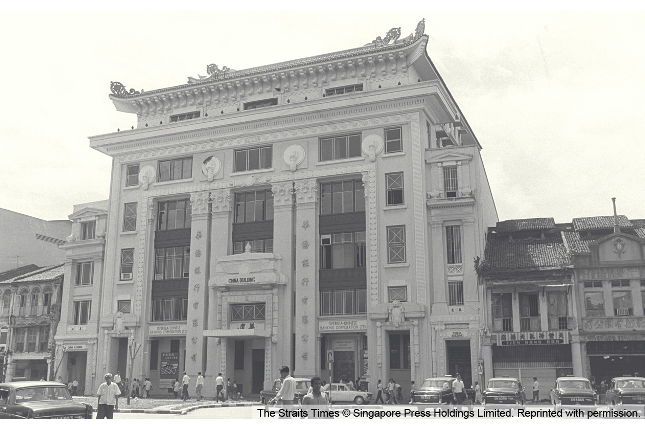

Oversea-Chinese Banking Corporation
OCBC bank was formed on 31st October 1932 in the midst of the great depression to serve the local community.
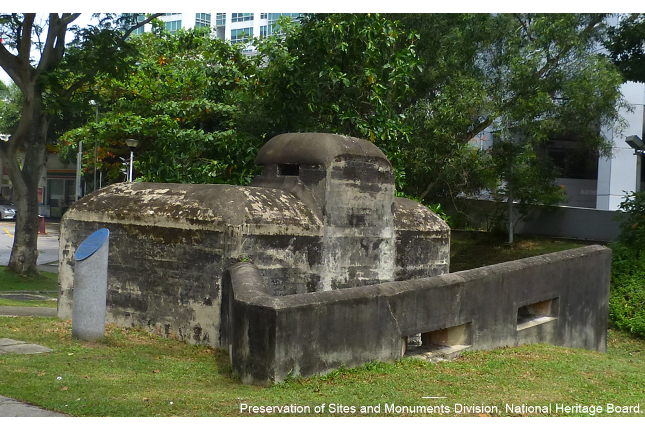

Pasir Panjang Machine-Gun Pillbox
Pillboxes were built in the 1930s to strengthen Singapore’s coastal defence as part of British preparation for a war in Singapore. The pillboxes were equipped with machine guns and positioned at strategic intervals to allow their fields of fires to overlap and reinforce each other.
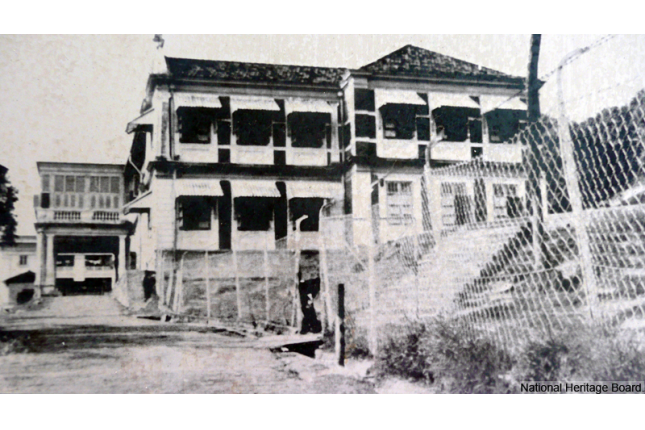

Pearl’s Hill School
Established in 1876 at Cross Street and formerly known as the Singapore Chinese Branch School, Pearl’s hill Primary School was among the pioneer batch of Government Schools set up by the colonial government. The school ceased it operations at its Pearl’s site on 31 December in 2001.
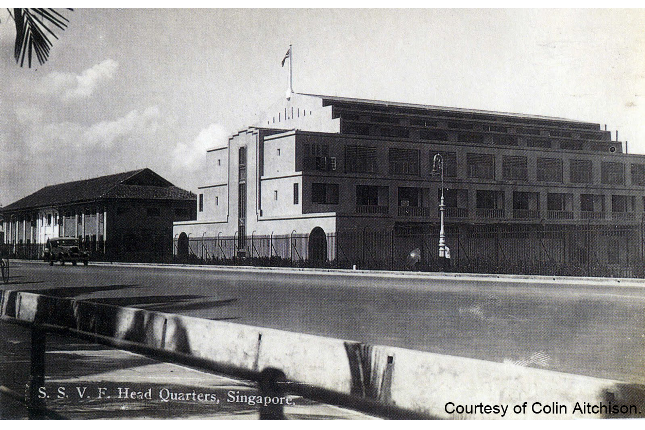

Peoples’ Defence Force Headquarters
In the early days of the SAF and Singapore’s independence, the Singapore Infantry Regiment and the PDF shouldered the duties of national defence. The Beach Road Army Camp played a significant role in the transformation.
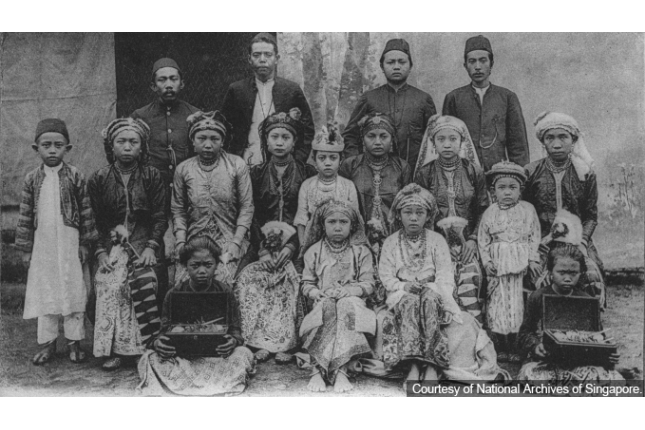

Pondok Peranakan Gelam Club
Registered on 4 April 1932, this club was set up by the Baweanese to cater for the needs of fellow immigrants from the Gelam province of Bawean Island, Indonesia. During the racial riots in 1945 and 1964, the Baweanese residents there were sheltered by their Chinese neighbours.
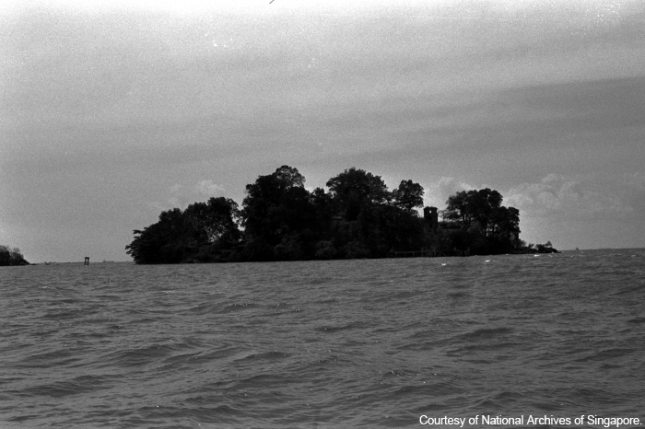

Pulau Sejahat
Pulau Sejahat, located off the north-eastern coast of Singapore, was designated as a British defence outpost. Its role was to protect the Johor Straits and the naval base at Sembawang.
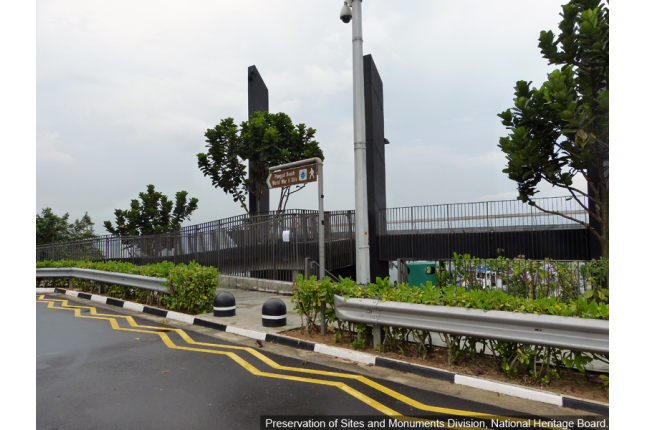

Punggol Beach Massacre
On 28 February 1942, some 400 Chinese Civilians, victims of the Sook Ching purge, were killed by the Japanese on this northeastern shore.
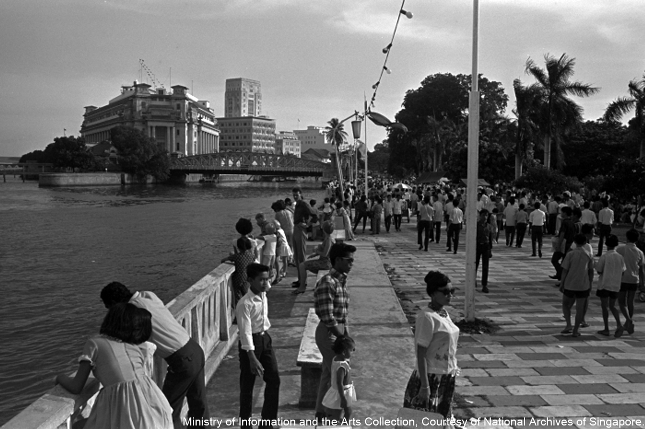

Queen Elizabeth Walk
This was the site of sporting activities in the early days and became popular with families. In 1953, as part of the Coronation Celebrations, the seafront promenade was refurbished and renamed Queen Elizabeth Walk.
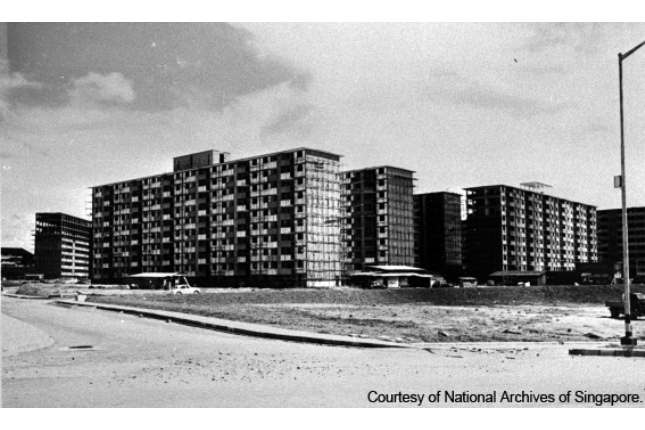

Queenstown Historic Marker
The Queenstown housing estate was one of the earliest housing estates developed around 1960 by the Singapore Improvement Trust(SIT) and subsequently the HDB. The British also set up a military camp “Buller Camp”, which was cleared in 1953.
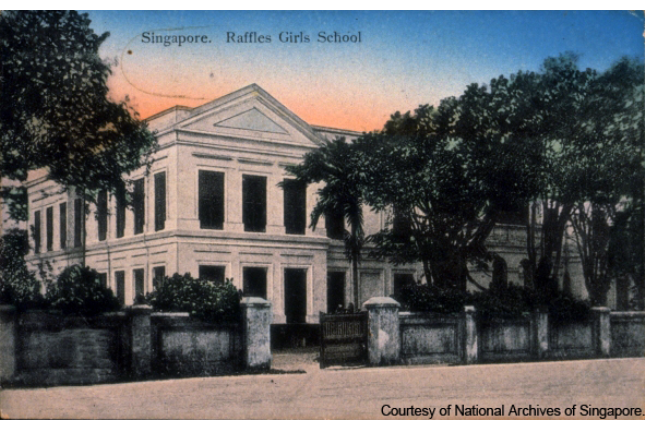
Raffles Girls' School
Established on 4 March 1844, Raffles Girls’ School first functioned as a moral development and vocational training class at the Singapore Institution. In 1928 it moved to a new building at Queen Street.
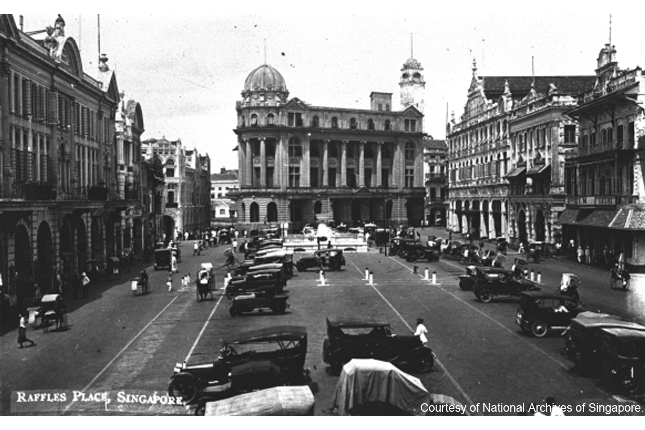

Commercial Square/Raffles Place
Raffles Place is the site of Singapore’s first commercial centre and became the business district for all communities. Sir Stamford Raffles drew up a Town Plan that allotted land use according to functional and ethnic divisions.
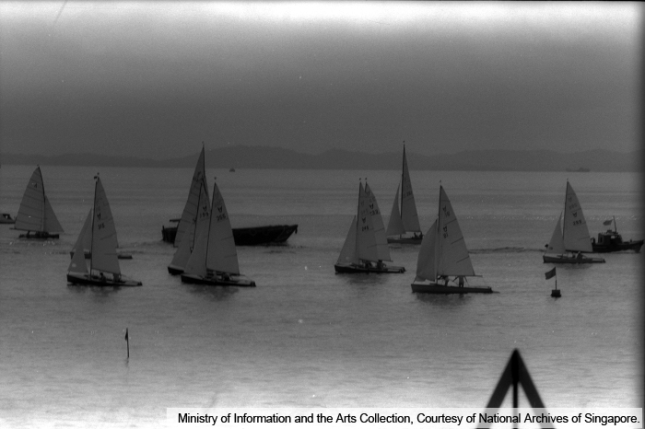

Republic of Singapore Yacht Club
Founded in 1826, this club became the Royal Singapore Yacht Club in 1922 under the patronage of the Prince of Wales, and was renamed the Republic of Singapore Yacht Club in 1967 with the first president of Singapore, Yusof bin Ishak as its patron.
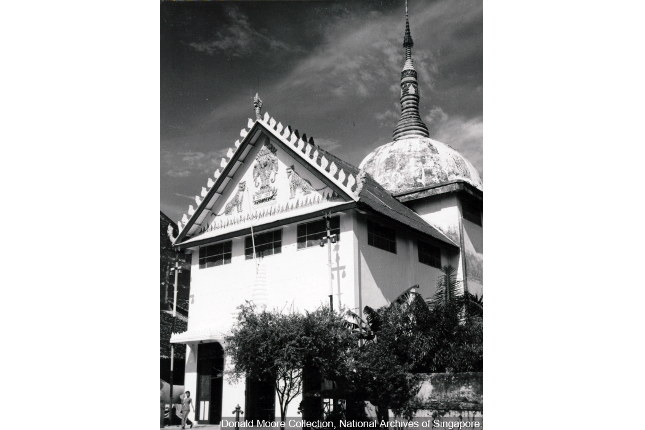

Sakya Muni Buddha Gaya Temple
Vutthisara, a monk from Thailand, founded the temple in 1927. Sakya Muni Buddha Gaya Temple is also known as the temple of 1,000 lights. These lights surround a 15-metre high statue of the reclining Buddha weighing 300 tonnes.
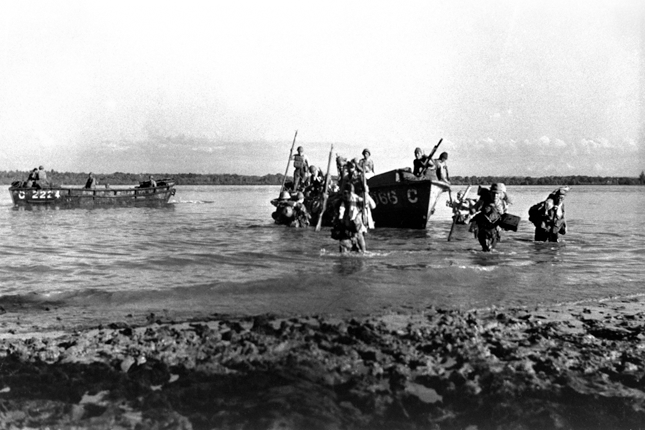

Sarimbun Beach Landing
Following the loss of Malaya to the Japanese, northwestern Singapore became the initial battleground between the Allied Army and the Japanese and this was one of the sites in the battle for Singapore.
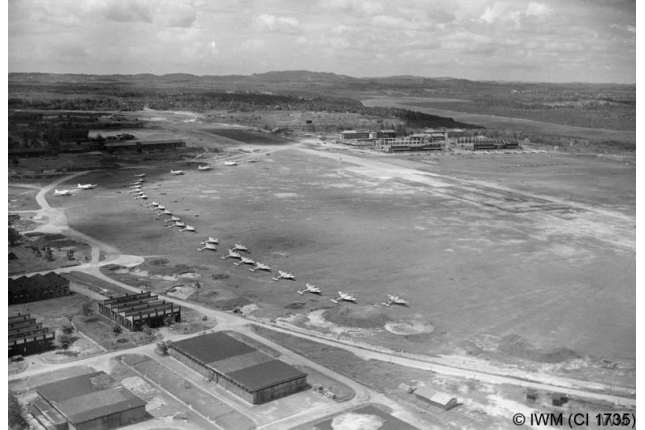

Seletar Airfield
Seletar Airfield was the British Royal Air Force’s main base in the Far East, and equipped to protect Singapore’s naval base in Sembawang. On 7 December 1941, an Allied plane that had taken off from Seletar tracked a Japanese fleet heading to Malaya in the South China Sea.
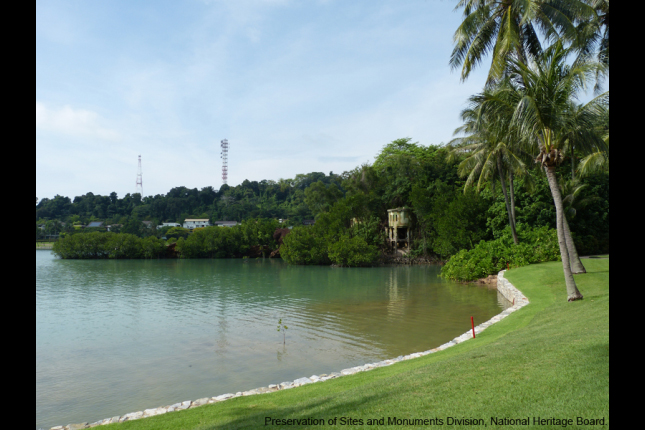

Sentosa Beach
Surrendered British gunners awaiting Japanese interment on Siloso Battery saw human bodies floating in Keppel Harbour and a number of these washed ashore on Pulau Blakang Mati (today's Sentosa Island).
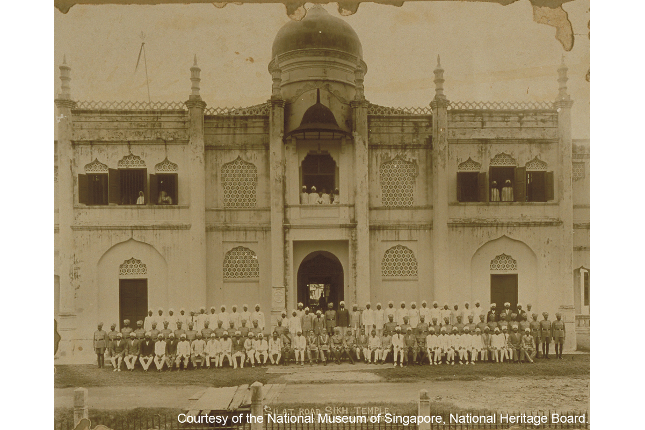

Silat Road Sikh Temple
Built in 1924, this temple was the first Sikh institution in Singapore to be constructed in the traditional style of a temple with domes and arches. During the Japanese Occupation, it sheltered Sikh orphans and widows.

Sime Road Camp
Sime Road Camp was the Combined Operations Headquarters of the British Army and Air Force from early December 1941 to 11 February 1942, until the Japanese advance forced the relocation of the headquarters from its compound in Sime Road to Fort Canning.
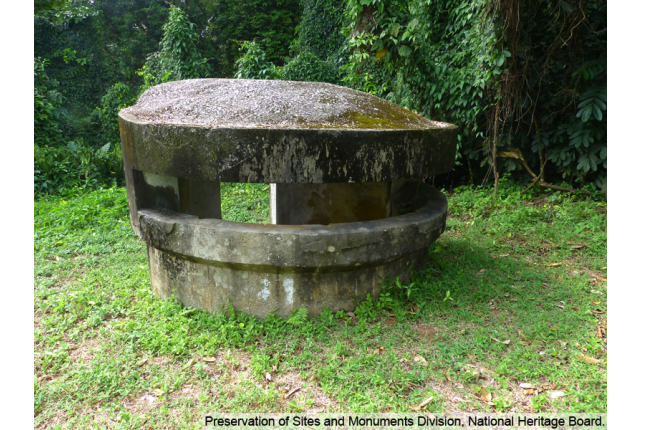

Sime Road Machine-Gun Pillbox
This pillbox was one of a network of pillboxes that provided overlapping and interlocking fields of fire to defend Flagstaff House which was used as the Combined Operations Headquarters of the British Army.
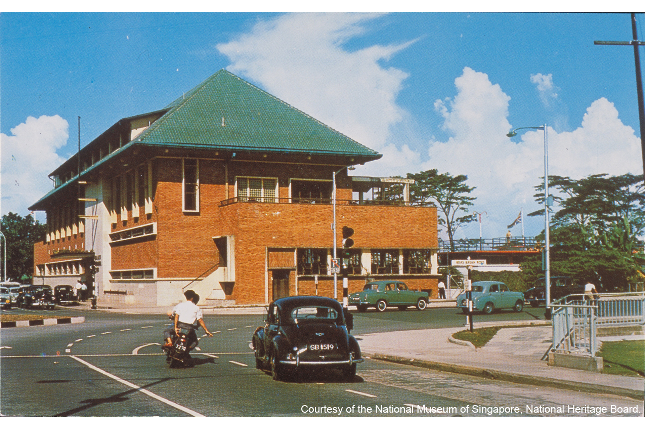

Singapore Armed Forces Warrant Officers and Specialists Club
The British Government built the clubhouse in 1951 for British non-commissioned officers. It was handed over to Singapore Government when the British pulled out in 1969.The SAF WOSE club was formed in 1974 and was formerly known as the SAF NCO Club until it was renamed in 1994.
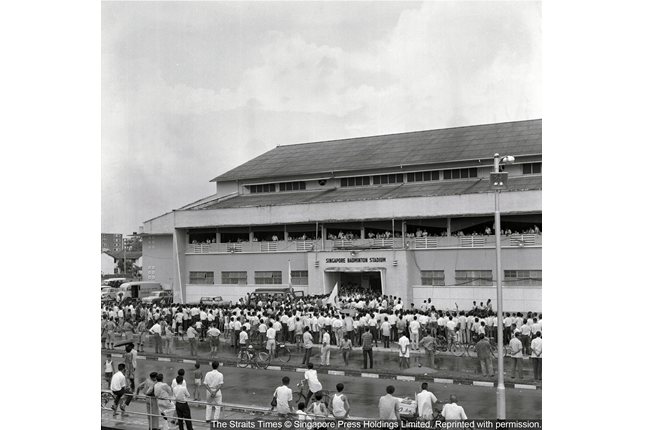

Singapore Badminton Hall
The Singapore Badminton Hall was built in 1951 as the venue for the Thomas Cup Tournament, and the third tournament held there at 1955. It was the site for the vote-counting for the Referendum on Singapore’s merger with Malaya, Sabah and Sarawak on 1 September 1962.
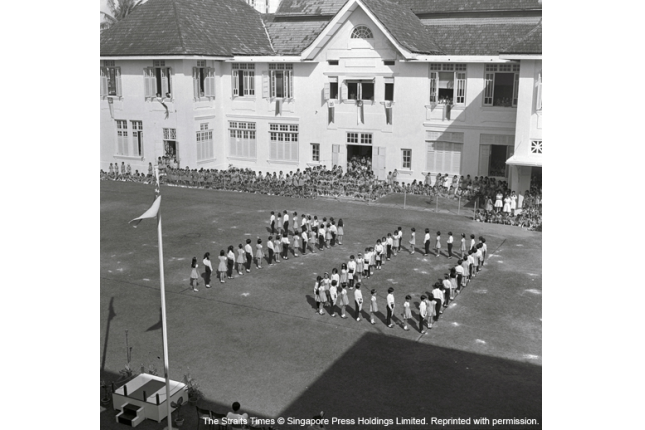

Singapore Chinese Girls’ School
This School was opened in 1899 under the auspices of a group of Straits Chinese, including Sir Song Ong Siang and Dr Lim Boon Keng. The Emerald Hill Site, which housed the school from 1925 to 1994, was the grounds of Dr Lim Boon Keng’s family home.
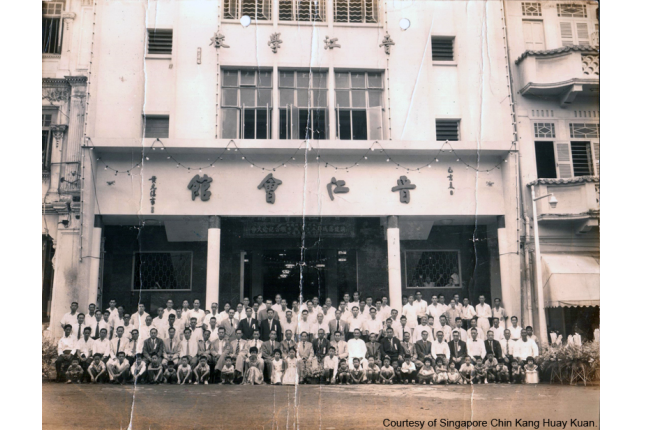

Singapore Chin Kang Huay Kuan
Established in 1918 by Chinese Immigrants from the Jin Jiang County of southern Fujian Province, it was the headquarters of the Overseas Chinese Mobilisation Council, formed in 1941 to help Singapore’s defence against the Japanese.
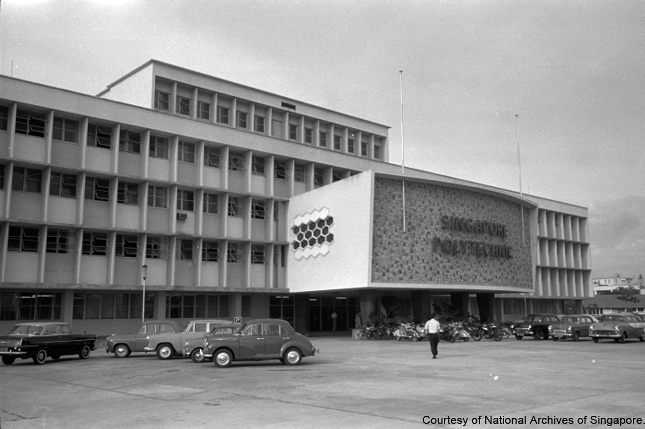

Singapore Polytechnic
The first institution to provide technical education in Southeast Asia, Singapore Polytechnic was once situated on this site. Established as an autonomous body on 27 October 1954, the polytechnic was set to train manpower needed for Singapore’s industries.

Sook Ching Inspection Centre
This site marks one of many temporary registration centres set up by the Kempeitai (Japanese Military Police) to screen anti-Japanese Chinese.
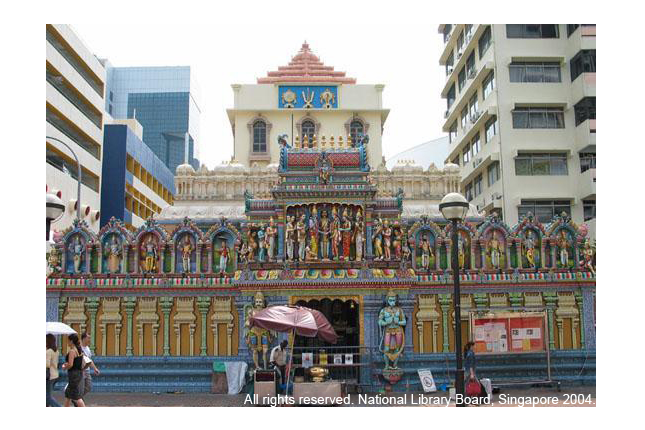

Sri Krishnan Temple
This temple was built in 1870 and is one of the oldest Hindu temples in Singapore.
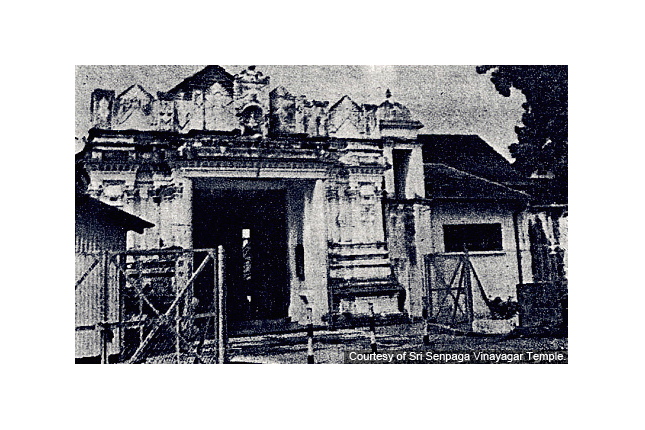

Sri Senpaga Vinayagar Temple
One of the oldest Hindu temples in Singapore, it was built in 1850. This temple was bombed during WWII and reconstructed in 1948.
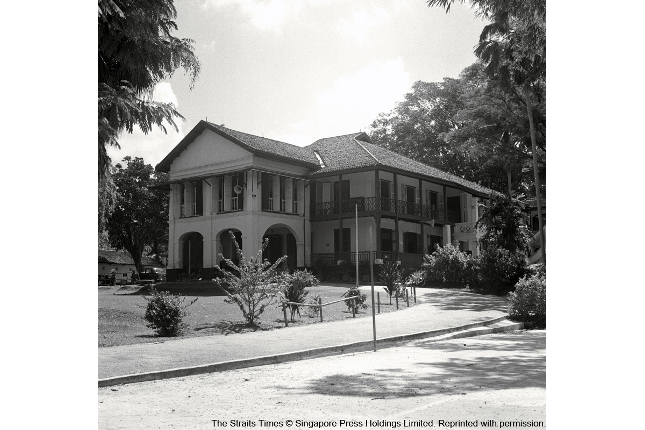

St. Margaret’s School
Singapore’s oldest girls’ school was established by Mrs Dyer of the London Missionary Society in 1842. “Mui Tsai”(girls sold to servitude) were taught Christian values, homemaking skills and given elementary English education here.
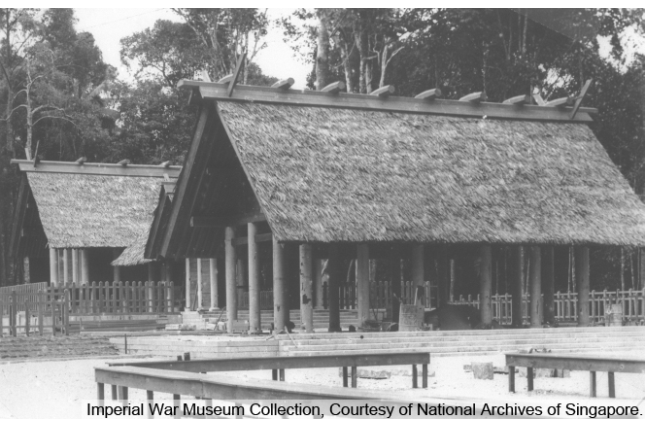

Syonan Jinja
Syonan Jinja, together with Syonan Chureito (a Japanese war memorial in Bukit Batok), was built in 1942 in memory of the Japanese soldiers who died fighting in the invasion of Singapore. It was named after Singapore, which was known as Syonan-To (“Light of the South”) during the Japanese Occupation (1942-1945).

Tan Tock Seng Hospital
Tan Tock Seng, a Malacca-born merchant and influential Chinese community leader and philanthropist founded the hospital on 25 July 1844. This Hospital played a significant role in the treatment of tuberculosis after WWII.
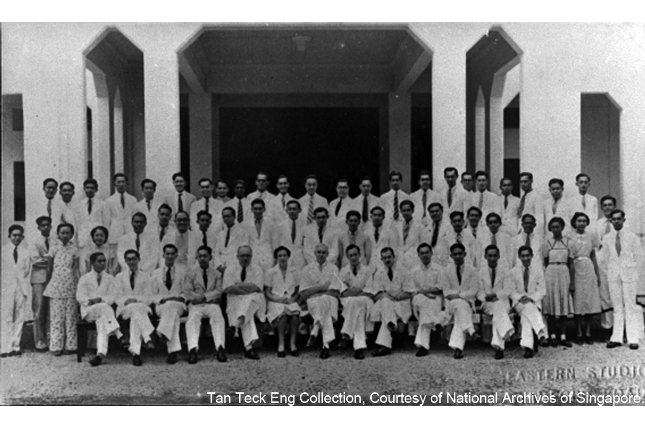

The First Public Dental Clinic and School
Dental Education and modern dentistry in Singapore began here in 1929. The original Clinic and Dental School of the King Edward VII college of Medicine had its beginnings on this site in the Norris Block of the General Hospital.
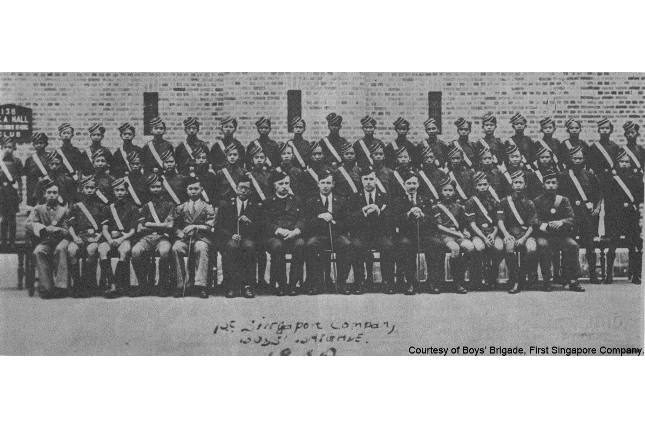

The Founding of Boys' Brigade in Singapore
Singapore’s 1st company of the Boy’s Bridgade was formed on 12 January 1930 at Prinsep Street Presbyterian Church by James Milner Fraser.

The Gate of Hope
At the small gate of the old Convent of the Holy Infant Jesus, many babies were abandoned, especially girls born in the “year of tiger” that were believed to bring bad luck to the family. The sisters adopted the babies and established the Home for Abandoned Babies.
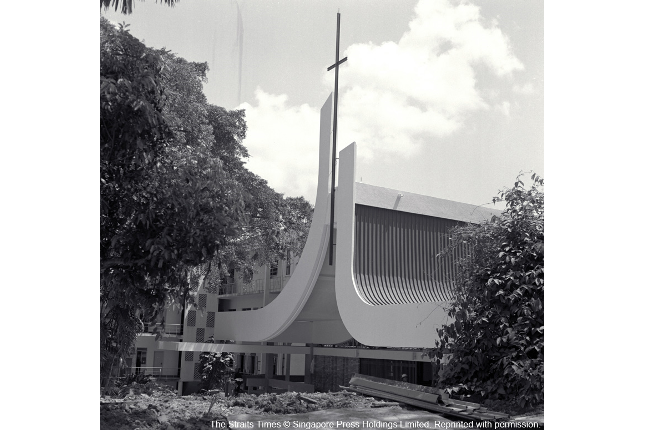

Trinity Theological College
Trinity Theological College was born out of the camaraderie and spirit of Christianity experienced by the heads of the Anglican, Methodist and Presbyterian Churches when they were interned at Changi Prison during the Japanese Occupation.
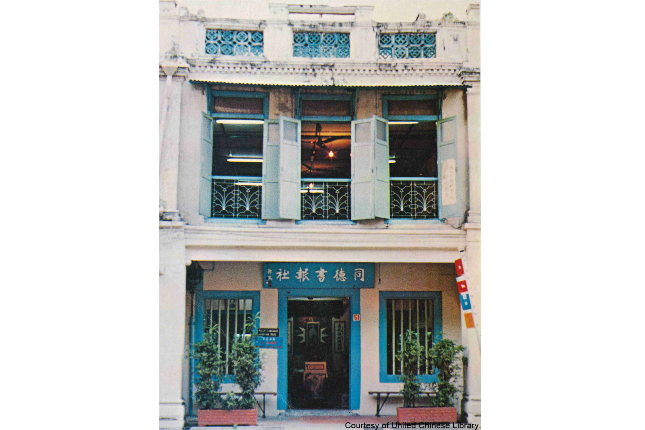

United Chinese Library
The United Chinese Library was inaugurated at Armenian Street on 8 August 1910 by Dr. Sun Yat Sen. Initially set up to promote general knowledge and culture, it also disseminated revolutionary ideas and generated support for the Chinese Revolution against the Manchu rulers.

United Overseas Bank
First known as the United Chinese Bank. It was founded on 6 August 1935 and opened for business on 1 october 1935 in Bonham Building. In 1965, it became the United Overseas Bank and on 19 October 1974, the 30-storeyed UOB Building was officially opened.
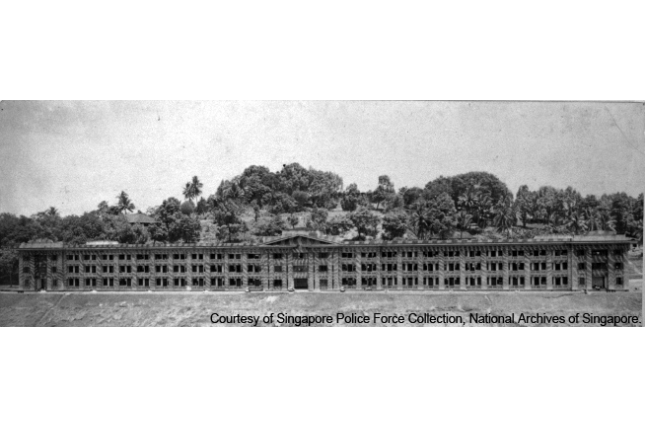

Former Upper Barracks
This 3-Storey building, along with the Lower Barracks, on Pearl’s Hill were built in 1934 specifically as residence for the Sikh Contingent of the Straits Settlement Police.
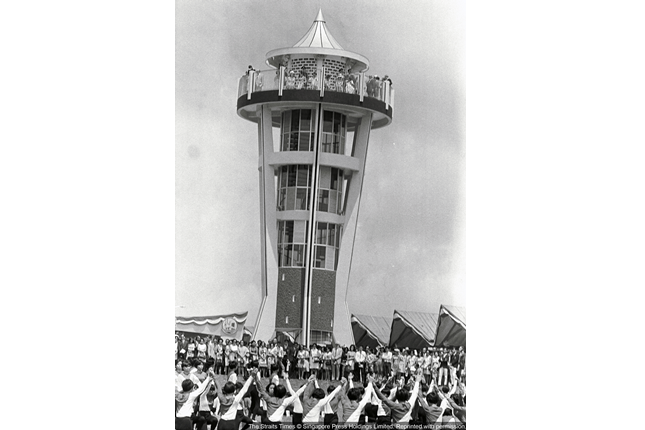

Upper Seletar Reservoir
Singapore’s third impounding Reservoir was built to meet the surge in water demand after WWI and was completed in 1940. Princess Alexandra officially opened it on 10 August 1969 when she presented Queen Elizabeth II during the 150th anniversary celebrations.
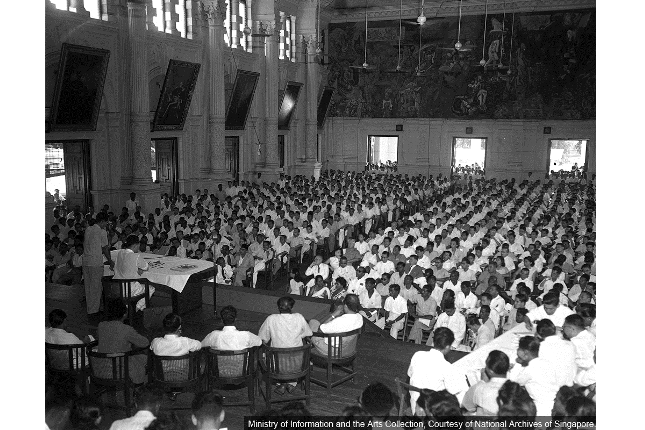

Victoria Memorial Hall
Designed by colonial engineer, John Bennett, the theatre portion of the Victoria Theatre and Concert Hall was built as a Town Hall in 1862 which housed the Municipal Offices
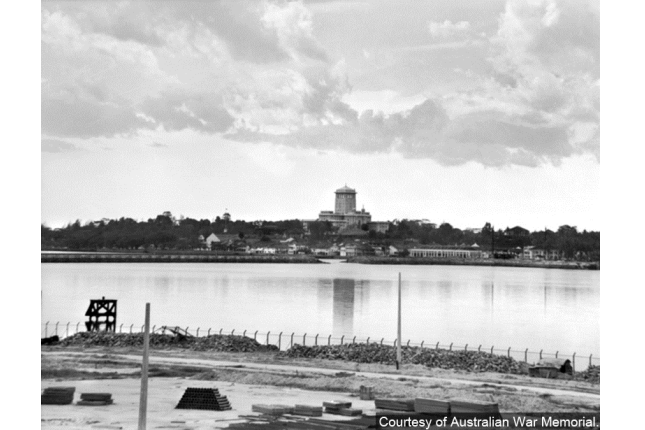

Withdrawal to Singapore
During the Second World War, the last Allied military troops crossed the Johore Straits and withdrew to Singapore via the Causeway on 31 January 1942, after losing the Malayan mainland to the Japanese.
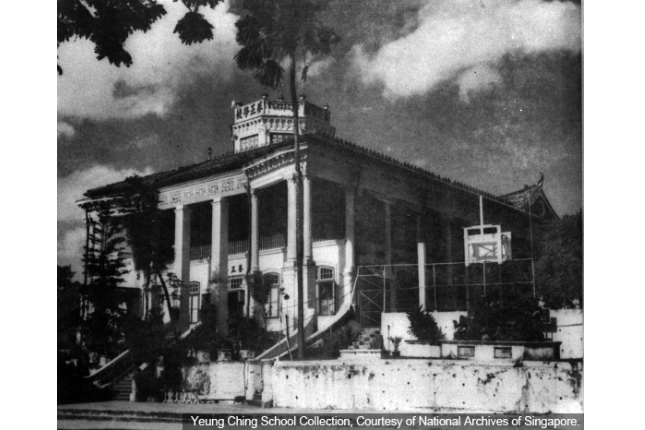

Yeung Ching School
Yeung Ching School began in 1905 as a private school for Cantonese children. Apart from conducting classes in the day, it offered night classes to children who were poor or overaged.
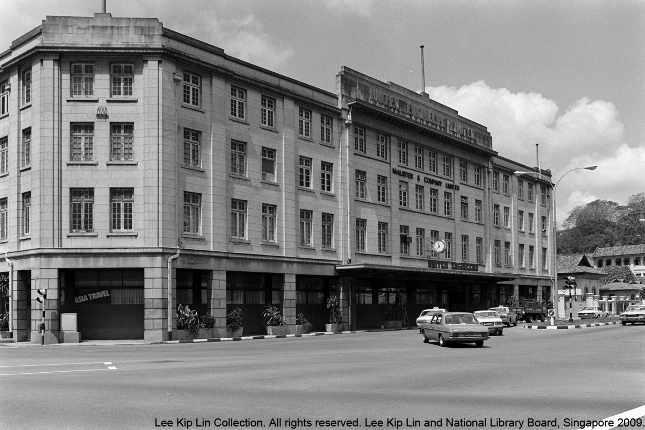

United Engineers Limited
Founded in 1912, United Engineers has been instrumental in designing and constructing many of the physical Structures in Singapore such as Supreme Court and Sentosa Monorail. The head office was demolished in 1991.

Lower Peirce Reservoir
This is Singapore’s second impounding reservoir. Originally known as the Kallang River Reservoir, it was renamed Peirce Reservoir in 1922 and again renamed Lower Peirce Reservoir in 1975.







